Faiss is a library for efficient similarity search and clustering of dense vectors. It contains algorithms that search in sets of vectors of any size, up to ones that possibly do not fit in RAM. It also contains supporting code for evaluation and parameter tuning. Faiss is written in C++ with complete wrappers for Python/numpy. Some of the most useful algorithms are implemented on the GPU. It is developed primarily at Meta’s Fundamental AI Research group.
Monthly Archives: March 2023
Phil 3.30.2023
Well that was quick – ChatPDF
IUI 2023
- Demo today! So of course I had to change some code at the last second.
- Had a nice chat yesterday with the author of this: Benefits of Diverse News Recommendations for Democracy: A User Study
- News recommender systems provide a technological architecture that helps shaping public discourse. Following a normative approach to news recommender system design, we test utility and external effects of a diversity-aware news recommender algorithm. In an experimental study using a custom-built news app, we show that diversity-optimized recommendations (1) perform similar to methods optimizing for user preferences regarding user utility, (2) that diverse news recommendations are related to a higher tolerance for opposing views, especially for politically conservative users, and (3) that diverse news recommender systems may nudge users towards preferring news with differing or even opposing views. We conclude that diverse news recommendations can have a depolarizing capacity for democratic societies.
- Some nice cites on Google Scholar, too
- Also interesting: Towards the Web of Embeddings: Integrating multiple knowledge graph embedding spaces with FedCoder
- The Semantic Web is distributed yet interoperable: Distributed since resources are created and published by a variety of producers, tailored to their specific needs and knowledge; Interoperable as entities are linked across resources, allowing to use resources from different providers in concord. Complementary to the explicit usage of Semantic Web resources, embedding methods made them applicable to machine learning tasks. Subsequently, embedding models for numerous tasks and structures have been developed, and embedding spaces for various resources have been published. The ecosystem of embedding spaces is distributed but not interoperable: Entity embeddings are not readily comparable across different spaces. To parallel the Web of Data with a Web of Embeddings, we must thus integrate available embedding spaces into a uniform space.
- Current integration approaches are limited to two spaces and presume that both of them were embedded with the same method — both assumptions are unlikely to hold in the context of a Web of Embeddings. In this paper, we present FedCoder— an approach that integrates multiple embedding spaces via a latent space. We assert that linked entities have a similar representation in the latent space so that entities become comparable across embedding spaces. FedCoder employs an autoencoder to learn this latent space from linked as well as non-linked entities.
- Our experiments show that FedCoder substantially outperforms state-of-the-art approaches when faced with different embedding models, that it scales better than previous methods in the number of embedding spaces, and that it improves with more graphs being integrated whilst performing comparably with current approaches that assumed joint learning of the embeddings and were, usually, limited to two sources. Our results demonstrate that FedCoder is well adapted to integrate the distributed, diverse, and large ecosystem of embeddings spaces into an interoperable Web of Embeddings.
Phil 3.29.2023
At IUI 2023. Rode my bike to the venue and got very rained on. And the forcast looks less than stellar to get some good riding in:

How to create a private ChatGPT with your own data
- It has some good stuff in it, including overlapping context windows, which I need to do. Also, it may make sense to break the query into vectors if it is multi-sentence. Keep the original, and then look at the relationship between the vectors. For example, “provide details” should probably be stripped as an outlier.
Phil 3.24.2023
5:30 John Wick Columbia Mall AMC
Prepping for IUI 2023
Sparks of Artificial General Intelligence: Early experiments with GPT-4
- Artificial intelligence (AI) researchers have been developing and refining large language models (LLMs) that exhibit remarkable capabilities across a variety of domains and tasks, challenging our understanding of learning and cognition. The latest model developed by OpenAI, GPT-4, was trained using an unprecedented scale of compute and data. In this paper, we report on our investigation of an early version of GPT-4, when it was still in active development by OpenAI. We contend that (this early version of) GPT-4 is part of a new cohort of LLMs (along with ChatGPT and Google’s PaLM for example) that exhibit more general intelligence than previous AI models. We discuss the rising capabilities and implications of these models. We demonstrate that, beyond its mastery of language, GPT-4 can solve novel and difficult tasks that span mathematics, coding, vision, medicine, law, psychology and more, without needing any special prompting. Moreover, in all of these tasks, GPT-4’s performance is strikingly close to human-level performance, and often vastly surpasses prior models such as ChatGPT. Given the breadth and depth of GPT-4’s capabilities, we believe that it could reasonably be viewed as an early (yet still incomplete) version of an artificial general intelligence (AGI) system. In our exploration of GPT-4, we put special emphasis on discovering its limitations, and we discuss the challenges ahead for advancing towards deeper and more comprehensive versions of AGI, including the possible need for pursuing a new paradigm that moves beyond next-word prediction. We conclude with reflections on societal influences of the recent technological leap and future research directions.
GPT Agents
- Fix TweetDownloader so it doesn’t try to look for empty strings – done
- Finish topic subsampling
- Download new db and put on laptop
SBIRs
- Expense trip – done
- Send notes to Aaron -done
- Close tasks and make some slides – done
Phil 3.22.2023

Artificial Influence: An Analysis Of AI-Driven Persuasion
- Persuasion is a key aspect of what it means to be human, and is central to business, politics, and other endeavors. Advancements in artificial intelligence (AI) have produced AI systems that are capable of persuading humans to buy products, watch videos, click on search results, and more. Even systems that are not explicitly designed to persuade may do so in practice. In the future, increasingly anthropomorphic AI systems may form ongoing relationships with users, increasing their persuasive power. This paper investigates the uncertain future of persuasive AI systems. We examine ways that AI could qualitatively alter our relationship to and views regarding persuasion by shifting the balance of persuasive power, allowing personalized persuasion to be deployed at scale, powering misinformation campaigns, and changing the way humans can shape their own discourse. We consider ways AI-driven persuasion could differ from human-driven persuasion. We warn that ubiquitous highlypersuasive AI systems could alter our information environment so significantly so as to contribute to a loss of human control of our own future. In response, we examine several potential responses to AI-driven persuasion: prohibition, identification of AI agents, truthful AI, and legal remedies. We conclude that none of these solutions will be airtight, and that individuals and governments will need to take active steps to guard against the most pernicious effects of persuasive AI.
This ties in to an earlier paper:
The Systemic Impact of Deplatforming on Social Media
- Deplatforming, or banning malicious accounts from social media, is a key tool for moderating online harms. However, the consequences of deplatforming for the wider social media ecosystem have been largely overlooked so far, due to the difficulty of tracking banned users. Here, we address this gap by studying the ban-induced platform migration from Twitter to Gettr. With a matched dataset of 15M Gettr posts and 12M Twitter tweets, we show that users active on both platforms post similar content as users active on Gettr but banned from Twitter, but the latter have higher retention and are 5 times more active. Then, we reveal that matched users are more toxic on Twitter, where they can engage in abusive cross-ideological interactions, than Gettr. Our analysis shows that the matched cohort are ideologically aligned with the far-right, and that the ability to interact with political opponents may be part of the appeal of Twitter to these users. Finally, we identify structural changes in the Gettr network preceding the 2023 Brasilia insurrections, highlighting how deplatforming from mainstream social media can fuel poorly-regulated alternatives that may pose a risk to democratic life.
GPT Agents
- Reversed the model list so more recent ones come first
- Finish the subsampling code
- AI Ethics/Watermarking review
SBIRs
- Download slide decks to laptop
- Pick up Aaron at 3:00
Phil 3.21.2023
First full day of Spring!
This post only focuses on prompt engineering for autoregressive language models, so nothing with Cloze tests, image generation or multimodality models. At its core, the goal of prompt engineering is about alignment and model steerability. Check my previous post on controllable text generation.
GPT Agents
- Sent the posters off to Staples
- Getting the embeddings for MAGA. Because I really don’t want to spend over $100 at OpenAI this month, I’m going to stop there and work on clustering, then export the db to the laptop
- Things are taking too long to get the clustering working. Wrote a procedure to take random tweets within a range that can be used for the clustering. The trick here is that all the values will need to be updated once the values are found:
DELIMITER $$
CREATE OR REPLACE PROCEDURE get_random_tweets(min_query_id INT, max_query_id INT, num_vals INT)
BEGIN
SELECT * FROM table_tweet AS t1
JOIN (
SELECT id FROM table_tweet
WHERE query_id >= min_query_id AND query_id <= max_query_id
ORDER BY RAND()
LIMIT num_vals
) as t2 ON t1.id=t2.id;
END $$
DELIMITER ;
SBIRs
- 9:15 Standup
- 9:30 tuning discussions with Rukan
- 10:30 meeting with Lauren and Aaron
- 1:00 MDA meeting
Phil 3.20.2023
Looks like you can prompt-tune some of the overconfidence out of the GPT-4

GPT Agents
- Pulling down embedddings and moderations. Kind of slow going. I think I need to do bigger pulls from the db, and then feed them slowly into the API. Done, after a few dumb errors. Much faster now
SBIRs
- 2:00 MDA meeting. Make sure to get the ball rolling on the commercialization meeting
- Prep for MC meeting. Need to do a first stab at slides – done
Phil 3.18.2023
GPT Agents
- Getting embeddings and moderations for tweets. Because there are so many of them, I need to send them in batches. Currently 100, but I think they can be larger. Try 500 next?
- Fix NarrativeMaps2 to use the same algo
- Change numbers in posters to bullets
Phil 3.17.2023
Phil 3. 16.2023
Google is introducing a first set of AI-powered writing features in Docs and Gmail to trusted testers. Rollout to begin with trusted users.
Lots of GPT-4 chatter. The demos look pretty incredible. Got my access!

SBIRs
- Add “to-GML” button that creates a network and saves a file to be imported into Gefi
- Create some pix!

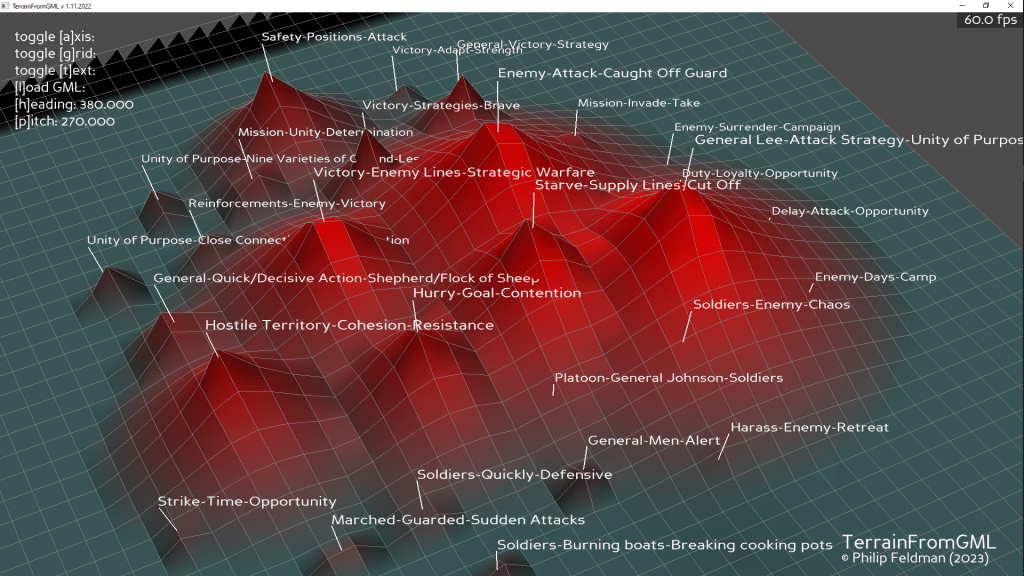
- 3:00 USMC prep with Aaron. Slides?
GPT Agents
- Once pix are done. Start on poster. Try to send off tomorrow
- Start processing embeddings for other tweets so there is more data to demo with
- If there is time, make some videos as a backup
Book
- 2:00 Meeting. Went well. I need to send some questions and answers that work in the context of the book – easy, medium, and hard
Phil 3.15.2023
What is Rumble? The streaming platform building an alternative internet
GPT Agents
- I realized that now with embeddings that I can revisit the “list of nearby xxx” approach to maps
- 4:00 or 5:00 meeting. Time zone issues
- Ping Antonio – done
SBIRs
- Run 100 stories each, cluster and label – done
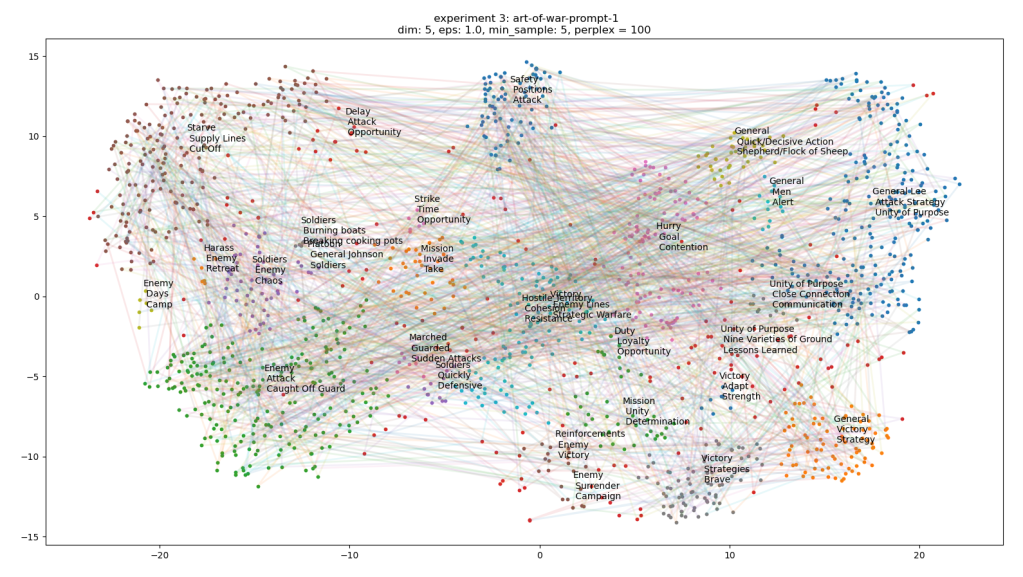
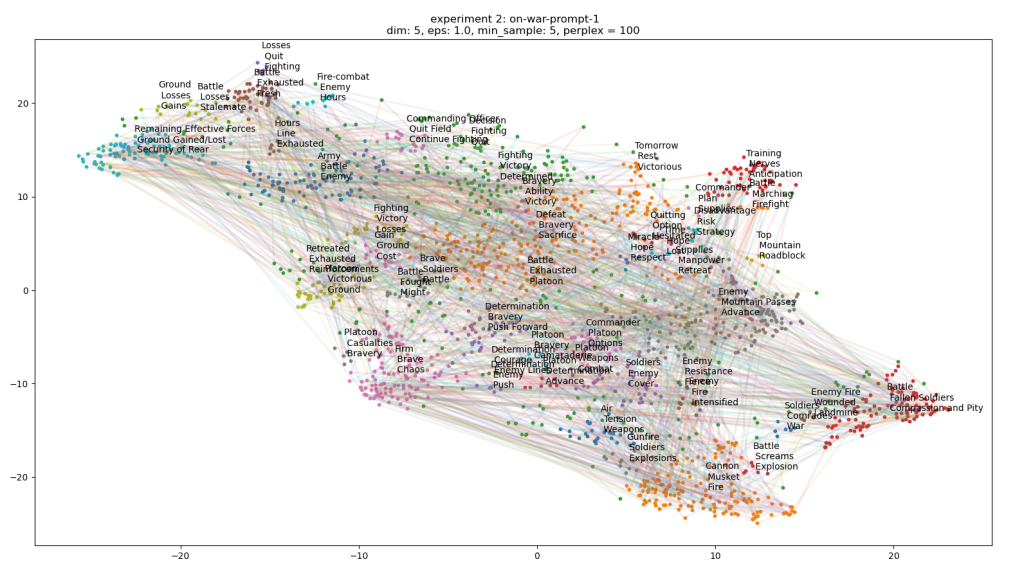
- Write the code that will connect the sentences for each of the stories and see if they pass through clusters in meaningful ways. I still wonder if just looking for distances between sentence (or summary) vectors would make more sense. Something to evaluate. Done
- Another thought is to average the narrative trajectory using an adjustable window. Something to try
- If things look reasonable, write code that creates a network graph out of the connected clusters, lay them out in Gephi, and render them. This all needs to be done before the 20th!
- Looking at the plots, things look very promising. I’ll try to generate networks tomorrow
Phil 3.14.23
Happy PI day, for all those irrational folks
AC service
Modern language models refute Chomsky’s approach to language
- The rise and success of large language models undermines virtually every strong claim for the innateness of language that has been proposed by generative linguistics. Modern machine learning has subverted and bypassed the entire theoretical framework of Chomsky’s approach, including its core claims to particular insights, principles, structures, and processes. I describe the sense in which modern language models implement genuine theories of language, including representations of syntactic and semantic structure. I highlight the relationship between contemporary models and prior approaches in linguistics, namely those based on gradient computations and memorized constructions. I also respond to several critiques of large language models, including claims that they can’t answer “why” questions, and skepticism that they are informative about real life acquisition. Most notably, large language models have attained remarkable success at discovering grammar without using any of the methods that some in linguistics insisted were necessary for a science of language to progress.
Alpaca: A Strong Open-Source Instruction-Following Model
- We introduce Alpaca 7B, a model fine-tuned from the LLaMA 7B model on 52K instruction-following demonstrations. Alpaca behaves similarly to OpenAI’s text-davinci-003, while being surprisingly small and easy/cheap to reproduce (<$600).
SBIRs
- Sprint planning – done
- Generate a set of prompts for stories using Sun Zu and Clausewitz and save them out in prompts – done
- Test the prompts in Narrative generator. Don’t forget about the later Babbage models
- Ran prompt1 using the Clausewitz context
- Run 100 stories each, cluster and label
- Write the code that will connect the sentences for each of the stories and see if they pass through clusters in meaningful ways. I still wonder if just looking for distances between sentence (or summary) vectors would make more sense. Something to evaluate.
- Another thought is to average the narrative trajectory using an adjustable window. Something to try
- If things look reasonable, write code that creates a network graph out of the connected clusters, lay them out in Gephi, and render them. This all needs to be done before the 20th!
- GPT BD tagup
GPT Agents
- I’d like to get the tweet text for the excel export, but I need to not plot that in the boxplot. This seems to be the answer?
Phil 3.13.2023
Pick up filters
GPT Agents
- Get speech stats and charts working in TweetEmbedExplorer – done! Interesting too. Here’s moderated speech for paxlovid vs ivermectin tweets
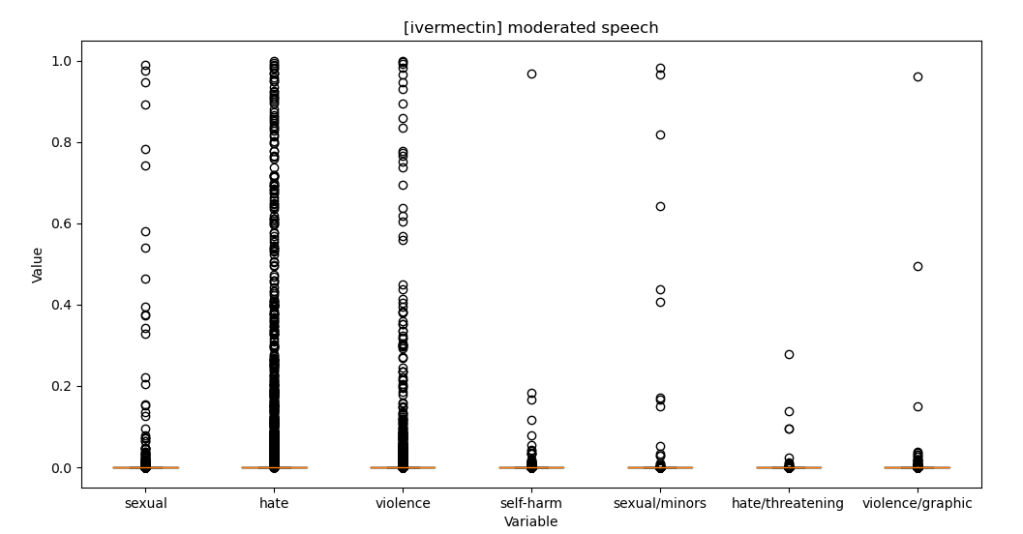
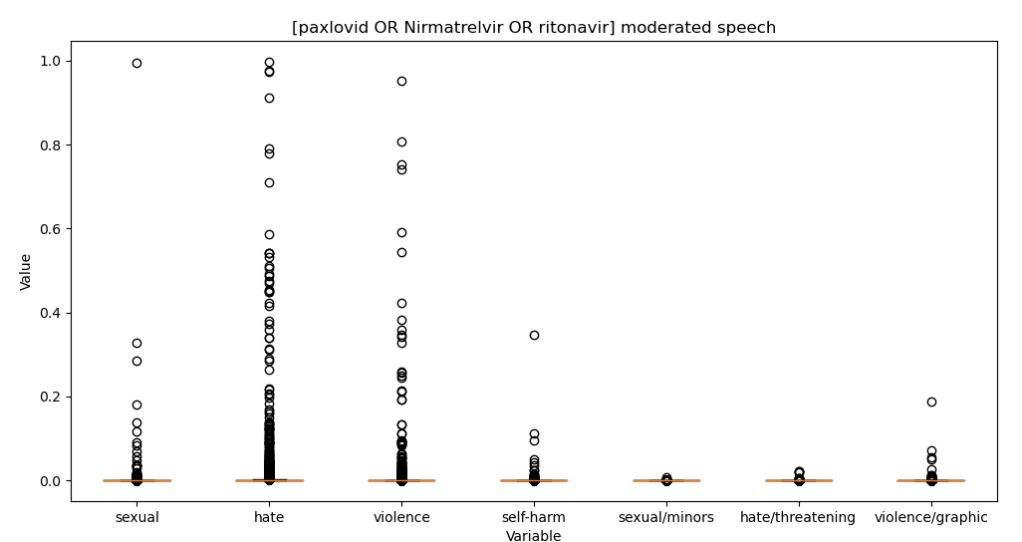
- Also fixed the embedding param storing code:

SBIRs
- Abstract was accepted at MORS!
- 9:00 Sprint demos – done. Need to put together stories
- 10:30 USMC prep meeting – nope
- 2:00 MDA meeting – done
- 3:00 JSC meeting – done
Phil 3.12.2022
Fine-tuning 20B LLMs with RLHF on a 24GB consumer GPU
- We are excited to officially release the integration of
trlwithpeftto make Large Language Model (LLM) fine-tuning with Reinforcement Learning more accessible to anyone! In this post, we explain why this is a competitive alternative to existing fine-tuning approaches. - Note
peftis a general tool that can be applied to many ML use-cases but it’s particularly interesting for RLHF as this method is especially memory-hungry! - If you want to directly deep dive into the code, check out the example scripts directly on the documentation page of TRL.
Phil 3.10.2023
Tasks
- Chores
- Groceries
- Yard -done
Book
- 2:00 Meeting – introduced some things but the software people didn’t show
SBIRs
- 10:GPT BD Meeting – demo went well
GPT Agents
- Get the “*” working
- Try the MCC memo to see how small texts work – pretty good!
- Add “clear” button – done. Helpful


You must be logged in to post a comment.