7:00 – 3:00 ASRC
- Register for Spring 2017
- Continuing with Sociophysics
- Cultural Dynamics
- The dissemination of culture a model with local convergence and global polarization Abstract: The basic premise is that the more similar an actor is to a neighbor, the more likely that that actor will adopt one of the neighbor’s traits. Unlike previous models of social influence or cultural change that treat features one at a time, the proposed model takes into account the interaction between different features. The model illustrates how local convergence can generate global polarization. Simulations show that the number of stable homogeneous regions decreases with the number of features, increases with the number of alternative traits per feature, decreases with the range of interaction, and (most surprisingly) decreases when the geographic territory grows beyond a certain size.
- This looks like a canonical document, like Ulrich Krause‘s Opinion dynamics and bounded confidence models, analysis, and simulation. Agents are clusters of traits.
- Speaking of which, here’s Krause talking about his models in a video.
- Searched for ‘flocking’ in the citing documents and found this:
How do cultural classes emerge from assimilation and distinction? An extension of the Cucker-Smale flocking model - In looking for recent work in the citing docs, found this 2016 article, which ties models back to observed data: Competing opinions and stubbornness: Connecting models to data
- This looks like a canonical document, like Ulrich Krause‘s Opinion dynamics and bounded confidence models, analysis, and simulation. Agents are clusters of traits.
- The dissemination of culture a model with local convergence and global polarization Abstract: The basic premise is that the more similar an actor is to a neighbor, the more likely that that actor will adopt one of the neighbor’s traits. Unlike previous models of social influence or cultural change that treat features one at a time, the proposed model takes into account the interaction between different features. The model illustrates how local convergence can generate global polarization. Simulations show that the number of stable homogeneous regions decreases with the number of features, increases with the number of alternative traits per feature, decreases with the range of interaction, and (most surprisingly) decreases when the geographic territory grows beyond a certain size.
- Social Choices and Popularity – skimmed, not appropriate
- Crowd-avoiding Dynamical Phenomena – skimmed, not appropriate
- Social Phenomena on Complex Networks
- Cultural Dynamics
- Integrity data
- Pulling all empty columns, and columns that contain encrypted data. Stupid slow and error prone. Going to write a quick app. It should be able to store and output data about all the useful columns in the tables. I should also be able to incorporate Gregg’s data dictionary (And look for toLower(“need definition”))
- Possibly output persistent queries for Java?
- Sparsity score?
- Column matches across tables?
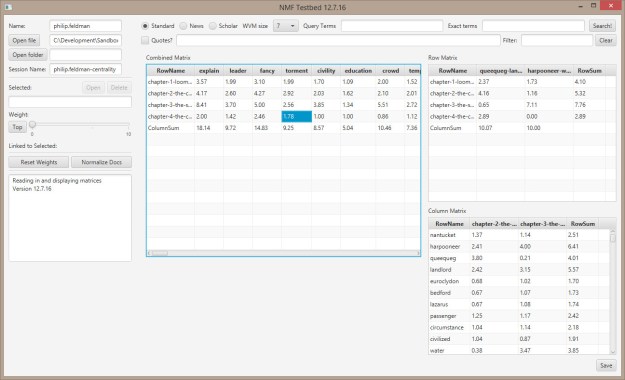
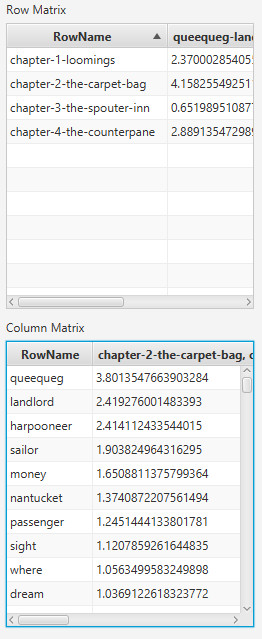
- Once master matrix is built, then use NMF to cluster columns for predictive capability
- Sprint review
- Ticket to fix my vpn access?

You must be logged in to post a comment.