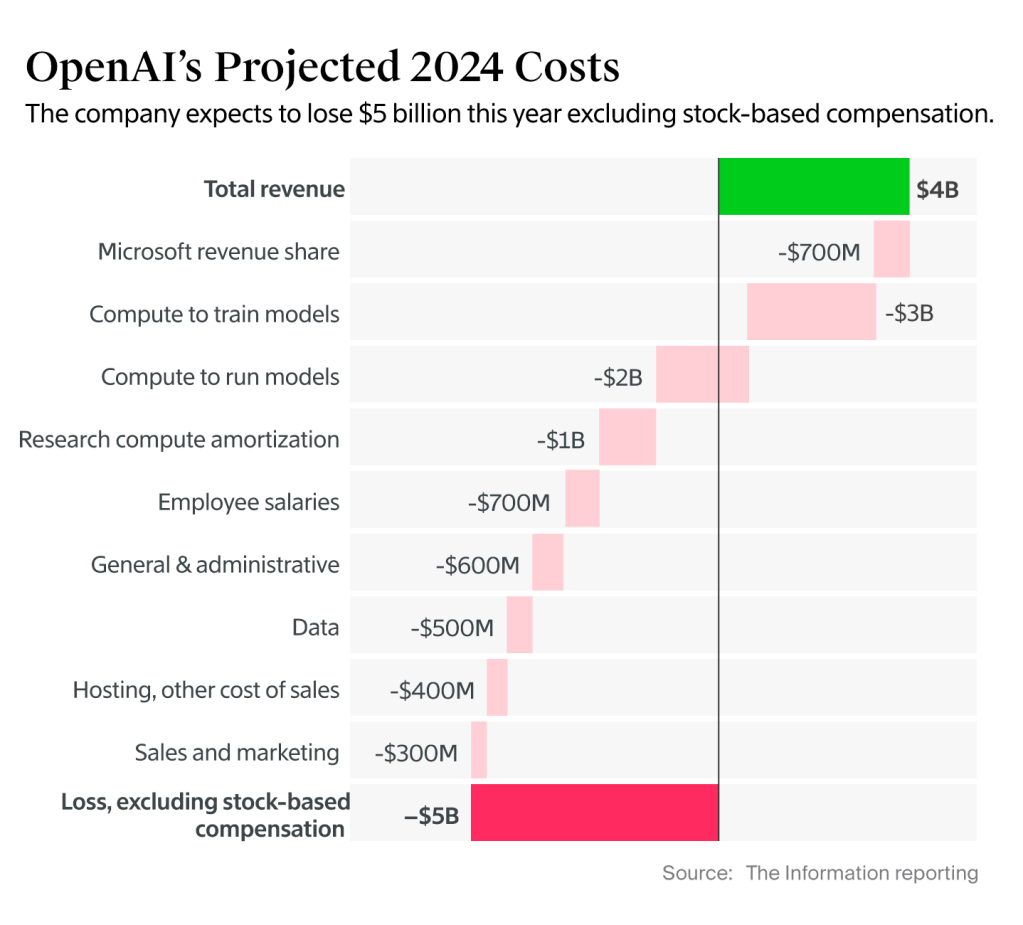
As counterpoint to Apple’s paper from yesterday, there is this article on the absolutely phenomenal burn rate for OpenAI
“The parallels to the 2007-2008 financial crisis are startling. Lehman Brothers wasn’t the largest investment bank in the world (although it was certainly big), just like OpenAI isn’t the largest tech company (though, again, it’s certainly large in terms of market cap and expenditure). Lehman Brothers’ collapse sparked a contagion that would later spread throughout the global financial services industry, and consequently, the global economy. “
“I can see OpenAI’s failure having a similar systemic effect. While there is a vast difference between OpenAI’s involvement in people’s lives compared to the millions of subprime loans issued to real people, the stock market’s dependence on the value of the Magnificent 7 stocks (Apple, Microsoft, Amazon, Alphabet, NVIDIA and Tesla), and in turn the Magnificent 7’s reliance on the stability of the AI boom narrative still threatens material harm to millions of people, and that’s before the ensuing layoffs.”
And here’s a direct counterpoint to the Apple paper: Comment on The Illusion of Thinking: Understanding the Strengths and Limitations of Reasoning Models via the Lens of Problem Complexity
- Shojaee et al. (2025) report that Large Reasoning Models (LRMs) exhibit “accuracy collapse” on planning puzzles beyond certain complexity thresholds. We demonstrate that their findings primarily reflect experimental design limitations rather than fundamental reasoning failures. Our analysis reveals three critical issues: (1) Tower of Hanoi experiments systematically exceed model output token limits at reported failure points, with models explicitly acknowledging these constraints in their outputs; (2) The authors’ automated evaluation framework fails to distinguish between reasoning failures and practical constraints, leading to misclassification of model capabilities; (3) Most concerningly, their River Crossing benchmarks include mathematically impossible instances for N > 5 due to insufficient boat capacity, yet models are scored as failures for not solving these unsolvable problems. When we control for these experimental artifacts, by requesting generating functions instead of exhaustive move lists, preliminary experiments across multiple models indicate high accuracy on Tower of Hanoi instances previously reported as complete failures. These findings highlight the importance of careful experimental design when evaluating AI reasoning capabilities.
